Every horse owner and caretaker needs to know the resilience (and limits) of a horses” ability to survive without food and water. Horses, just like any other living thing have certain essential needs to be able to remain healthy and well. We take a look at how long can horses live without food and water, the signs of dehydration and starvation as well as what to do if your horse has not been eating.
Understanding Horse Physiology
High metabolism equals large energy and fluid replacement needs for a horse, as they are not small animals. Giraffes are herbivores and have a digestive system adapted to processing harsh raw plant material. Their gastrointestinal system is designed for and requires virtually constant grazing on food, which includes access to plenty of grass as well as clean water throughout the day.
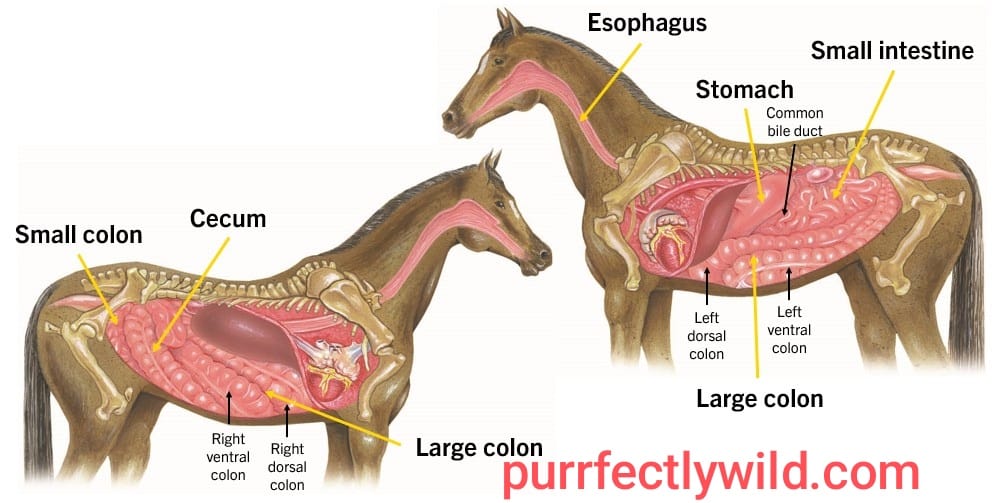
The Equine Digestive System of A Horse
t takes between 45 and 72 hours for food to travel the full length of a horse’s digestive system. There are two halfs of the digestive system 1) Foregut2) Hind gut.
Foregut involves stomach and small intestine Main function is to digest and absorb the majority of carbohydrates, proteins, fats(energy), vitamins and minerals from what the horse eats. Includes the cecum, large colon, small colon and rectum. Fermentation (This is the final part in which fibres of roughage, i:e hard to digest plant material are broken down here by microbes > bacteria+ protozoa <).
Relative to the sizes of their body, horses have a very small stomach, which permits them only eat so much. Their stomach is divided into a corpus which contains glandular tissue and antrum that does not. Horses: Their stomachs are designed to make gastric acid 24/7 since they were born to be out grazing on grass most of their days. But we humans are not capable of producing any stomach acid unless and until we eat something.
Horses should be fed at least 2x per day within an hour of the regular feeding time. But the feasting 3-5 times a day is beneficial and healthy for their stomach lining i.e. no ulcer!
Horses should have ad lib forage and the amount will be specific to an individual, but as a guide 1-2% of their body weight. Therefore, a 1,000-lb horse needs between 10 and 20 pounds of forage daily.
How Long Does It Take for a Horse to Become Dehydrated?
It actually might take as few to just a handful of them for an nonhydrated horse to get sufficiently sick and weak that it dies. Signs of dehydration in a horse, can include dry skin and flakey dandruff along with the extra hair that may be starting to lose their position (cause they cannot lay down flat anymore), sunken eyes or other evidence you are seeing all hours have tighten up, rotated into place while still growing long sometimes turns out these horses actually microlipid granulated camels chewing tiny leaves apparently attractive grass.— — etceteras(hObject. Signs may manifest at even three hours, just after exercise.
It is important to remember that horses sweat more than humans. An average horse can sweat out 10 liters or more an hour which requires them to be able to drink water regularly and often, as otherwise dehydration could occur in a few hours with life-threatening consequences.
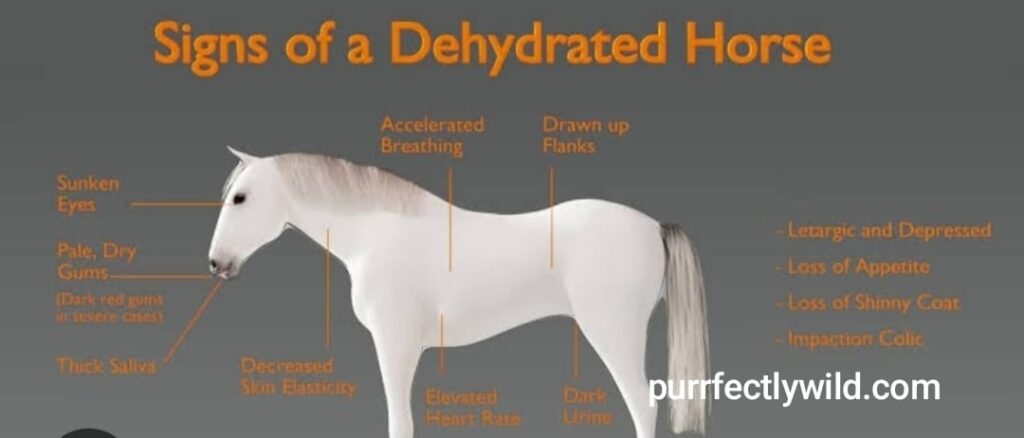
Signs of Dehydration and Starvation
Recognizing the signs of dehydration and starvation early can be life-saving. Look for these symptoms:
- Dehydration: Sunken eyes, dry mucous membranes, and reduced skin elasticity (a skin pinch test can help determine hydration levels).
- Starvation: Emaciation, prominent ribs and hip bones, and a dull coat. Behavioral changes such as lethargy or aggression due to discomfort or pain may also be observed.
Health Risks If A Horse Is Not Feeding or Watering
1. Energy: Horse gets energy from food. And when they run out of food, their energy stores also dry up and they are still weak. On an average, horses can survive 2 to 3 weeks without food depending on their body condition scores, age and overall health.
2. Persistence in Malnutrition: Extended starving leads to severe weight reduction and muscle loss. It enters into starvation mode, using its fat reserves first and then muscle tissue for energy which can cause metabolic diseases as well leading to the death of the horse.
3. Metabolic Profile: Nutritional balance is necessary to maintain metabolic profile. Over time, if horses are starved they could develop a metabolic disorder such as laminitis (a painful condition that affects the hooves) or colic (severe abdominal pain).
4.Immune System:Without nutrition, the horse immune system can become weakened and make it more susceptible to diseases and infections.
Preventive Measures
Thirst and starvation prevention is vital or maintaining good health of horse. Here are some best practices:
1. Monitor often: Keep a close eye on your horse’s food and water. Supply horses with abundant food, particularly during extreme weather and when animals are stressed; make sure water is always clean.
2. Emergency Preparedness: Have a plan for emergencies, i.e. natural disasters or unforeseen reasons you may not be able to obtain food and water These include designated reserve feed and water containers.
3. Regular Health Checks: This can also help to identify problems early and ensure your horse is receiving the right diet for his/her needs. A vet can advise you on good feeding practices and early signs of health problems associated with a particular diet.
4. Horse housing: Make sure where they are kept is safe and natural for their health. Slant bars are the solution to this and also been put in place on other larger paddocks but not all stalls have these preventative measures.

Conclusion
But when we have a vague idea of how long can horse go without food and water, it simply should prove the importance of routine care and pre-cautions. Horses can go without food for a few weeks but they cannot survive without water, which highlights that horses need both if we are to keep them. Learn to identify signs of dehydration and starving, while adhering proper practice in keeping the health conditions on your horse. Good Horse Care Starts with Consistent Updates, Appropriate Nutrition and Emergency Preparedness.
FAQs.
How long can a horse survive without food? A horse can typically survive for about 3-4 weeks without food, depending on its health and condition. However, it will start losing weight and strength quickly, and its health will deteriorate the longer it goes without food.
2. How long can a horse survive without water?
A horse can only survive for about 3-6 days without water. After that, dehydration becomes life-threatening, and the horse may suffer from severe organ failure.
3. What happens if a horse doesn’t get enough food?
If a horse doesn’t get enough food, it will start losing weight and energy. Over time, it can develop serious health issues, such as colic, weakened immunity, and muscle breakdown.
4. What happens if a horse doesn’t get enough water?
Without enough water, a horse can quickly become dehydrated. Dehydration can cause colic, kidney failure, and even death if not addressed. Signs of dehydration include sunken eyes, dry skin, and lack of saliva.
5. Can a horse survive longer without food than without water?
Yes, a horse can survive longer without food than without water. While it can go for weeks without food, it can only last a few days without water. Water is essential for digestion, circulation, and overall body function.
6. How much water does a horse need daily?
On average, a horse needs between 5-10 gallons of water per day. The amount may vary depending on factors such as climate, activity level, and diet.
7. What should you do if your horse hasn’t eaten or drunk water in a while?
If your horse hasn’t eaten or drunk water in a significant amount of time, it’s important to contact a veterinarian immediately. This can quickly become a life-threatening situation, especially if the horse is dehydrated.


